1. Python Scripts
Scripts and codes using Python language.
Reload all reads
Reload all Read nodes in the graph.
def reloadAllReads():
nodes = [
node for node in nuke.allNodes(recurseGroups=True)
if node.Class() == 'Read'
]
for node in nodes:
node.knob('reload').execute()
Reload all Blinks
Reload all BlinkScript nodes in the graph.
def reloadAllBlinks():
nodes = [
node for node in nuke.allNodes(recurseGroups=True)
if node.Class() == 'BlinkScript'
]
for node in nodes:
nuke.show(node)
node.knob('reloadKernelSourceFile').execute()
node.hideControlPanel()
Path Explorer
Open filename's path on the explorer from every selected Read or Write nodes.
def pathExplorer():
import os, subprocess
sel = nuke.selectedNodes()
for node in sel:
if node.Class() == 'Read' or node.Class() == 'Write':
FILE = nuke.filename(node)
PATH = os.path.dirname(FILE)
subprocess.Popen('explorer "{}"'.format(PATH.replace('/', '\\')))
Write Folder Creator
Creates all the nonexistent folders from the file directory of selected Write nodes.
def writeFolderCreator():
import os
nodes = nuke.selectedNodes('Write')
if not nodes:
nuke.message('select some write node')
return None
for node in nodes:
FILE = nuke.filename(node)
PATH = os.path.dirname(FILE)
if not os.path.isdir(PATH):
nodeName = node.knob('name').getValue()
if nuke.ask(
'{0} \n\n {1} \n\n'.format(nodeName, PATH) +
'this path does not exist. Would like to create this?'
):
os.makedirs(PATH)
Set Multiple Knobs
Set multiple knobs from multiple selected nodes. (separate arguments by comma)
Example:
| knob name | first, origfirst, last, origlast |
| value | 1, 1, 120, 120 |
it define the first and the last frame of all selected Read nodes.
def setMultipleKnobs():
import ast
nodes = nuke.selectedNodes()
if not nodes:
nuke.message('select some node')
return None
classes = set()
for node in nodes:
classes.add(node.Class())
enumClasses = ' '.join(['all'] + list(classes))
p = nuke.Panel('set multiple knobs')
p.addEnumerationPulldown('node class', enumClasses)
p.addSingleLineInput('knob name', '')
p.addSingleLineInput('value', '')
c = p.show()
if c:
nodeClass = p.value('node class')
knobName = [e.lstrip() for e in p.value('knob name').split(',')]
try:
value = list(ast.literal_eval(p.value('value')))
except:
value = [eval(p.value('value'))]
if len(knobName) != len(value):
nuke.message(
"The knobName's field and the value's field " +
"must have the same number of arguments"
)
return None
for node in nodes:
if node.Class() == nodeClass or nodeClass == 'all':
for index in range(len(knobName)):
node.knob(knobName[index]).setValue(value[index])
2. Blink Scripts
Scripts and codes using BlinkScript language.
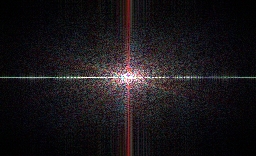
Discrete Fourier Transform
Discrete Fourier transform (DFT) for frequency domain analysis/processing and spatial-frequency filtering.

//defining the type for complex numbers
typedef float2 complex;
//Calculate complex number's exponential based on Euler's formula
inline complex cExp(float a) {
return a < 0
? complex(cos(fabs(a)), - sin(fabs(a)))
: complex(cos(a), sin(a));
}
kernel DFT: ImageComputationKernel<eComponentWise> {
Image<eRead, eAccessRandom, eEdgeNone> in;
Image<eWrite> out;
param:
bool centerKernel;
local:
float N1, N2;
void define() {
defineParam(centerKernel, "center kernel", true);
}
void init() {
N1 = in.bounds.width();
N2 = in.bounds.height();
}
void process(int2 p) {
ValueType(in) x(0);
complex X(0);
float w1 = centerKernel ? fmod(p.x + N1*0.5f, N1) : p.x;
float w2 = centerKernel ? fmod(p.y + N2*0.5f, N2) : p.y;
for(int n1 = 0; n1 < N1; n1++){
for(int n2 = 0; n2 < N2; n2++){
x = in(n1, n2);
X += x*cExp(-2.0f*PI*(w1*n1/N1 + w2*n2/N2));
}
}
// normalization
X *= 1/sqrt(N1*N2);
// output
out() = X.x + X.y;
}
};
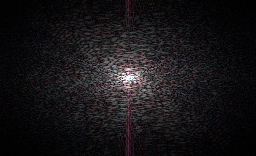
Inverse Discrete Fourier Transform
Inverse discrete Fourier transform for frequency domain analysis/processing and spatial-frequency filtering.

//defining the type for complex numbers
typedef float2 complex;
//Calculate complex number's exponential based on Euler's formula
inline complex cExp(float a){
return complex(cos(a), sin(a));
}
kernel DFTi: ImageComputationKernel<eComponentWise> {
Image<eRead, eAccessRandom, eEdgeNone> in;
Image<eWrite> out;
param:
bool centeredKernel;
local:
float N1, N2;
void define() {
defineParam(centeredKernel, "centered kernel", true);
}
void init() {
N1 = in.bounds.width();
N2 = in.bounds.height();
}
void process(int2 p) {
ValueType(in) X(0);
complex x(0);
float n1 = N1 - p.x;
float n2 = N2 - p.y;
for(int k1 = 0; k1 < N1; k1++) {
for(int k2 = 0; k2 < N2; k2++) {
X = centeredKernel
? in(fmod(k1 + N1*0.5f, N1), fmod(k2 + N2*0.5f, N2))
: in(k1, k2);
x += X*cExp(2.0f*PI*(n1*k1/N1 + n2*k2/N2));
}
}
// normalization
x *= 1.0f/sqrt(N1*N2);
// output
out() = x.x + x.y;
}
};
Inf and NaN filter
A nonlinear filter, which removes Inf and NaN artifacts.


#define isInf(value) value/value != 1 ? true : false
#define isNaN(value) value != value ? true : false
kernel infNanFilter: public ImageComputationKernel<eComponentWise> {
Image<eRead, eAccessRanged2D, eEdgeClamped> in;
Image<eWrite, eAccessPoint> out;
param:
float radius;
void define() {
defineParam(radius, "radius", 1.0f);
}
void init() {
in.setRange(-radius, -radius, radius, radius);
}
void process() {
float current = in(0, 0);
float ranged;
float result = 0;
int count = 0;
if(isInf(current) || isNaN(current)) {
for(int j = - radius; j <= radius; j++) {
for(int i = - radius; i <= radius; i++) {
ranged = in(i, j);
if(isInf(ranged) || isNaN(ranged)) continue;
else{
result += in(i, j);
count++;
}
}
}
if(result != 0) out() = result/count;
else out() = 0;
}
else out() = current;
}
};
Median Saturation
Adjust the levels of saturation statistically, using median value.


kernel medianSaturation: ImageComputationKernel<ePixelWise> {
Image<eRead, eAccessPoint, eEdgeNone> in;
Image<eWrite> out;
param:
bool AM, GM, HM;
float saturation;
bool alpha;
void define() {
defineParam(AM, "arithmetic mean", false);
defineParam(GM, "geometric mean", false);
defineParam(HM, "harmonic mean", false);
defineParam(saturation, "saturation", 1.0f);
defineParam(alpha, "includes alpha", false);
}
void process() {
float medi, ami, gmi, hmi;
SampleType(in) color(0);
SampleType(in) result(0);
color = in();
ami = (color.x + color.y + color.z)/3.0f;
gmi = pow(color.x*color.y*color.z, 1.0f/3.0f);
hmi = 3.0f*pow(1.0f/color.x + 1.0f/color.y + 1.0f/color.z, -1.0f);
if(!AM and !GM and !HM) {
float l[3] = {color.x, color.y, color.z};
medi = median(l, 3);
} else if(AM and !GM and !HM) {
float l[4] = {color.x, color.y, color.z, ami};
medi = median(l, 4);
} else if(!AM and GM and !HM) {
float l[4] = {color.x, color.y, color.z, gmi};
medi = median(l, 4);
} else if(!AM and !GM and HM) {
float l[4] = {color.x, color.y, color.z, hmi};
medi = median(l, 4);
} else if(AM and GM and !HM) {
float l[5] = {color.x, color.y, color.z, ami, gmi};
medi = median(l, 5);
} else if(AM and !GM and HM) {
float l[5] = {color.x, color.y, color.z, ami, hmi};
medi = median(l, 5);
} else if(!AM and GM and HM) {
float l[5] = {color.x, color.y, color.z, gmi, hmi};
medi = median(l, 5);
} else if(AM and GM and HM) {
float l[6] = {color.x, color.y, color.z, ami, gmi, hmi};
medi = median(l, 6);
} else {
float l[3] = {color.x, color.y, color.z};
medi = median(l, 3);
}
result = (1 - saturation)*medi + saturation*color;
if(!alpha) {
result.w = color.w;
}
out() = result;
}
};
Normalize
Normalize RGB channels.


kernel Normalize: ImageComputationKernel<ePixelWise> {
Image<eRead, eAccessPoint> in;
Image<eWrite> out;
void process() {
SampleType(in) n(in());
float normal = sqrt(pow(n.x, 2) + pow(n.y, 2) + pow(n.z, 2));
if(normal != 0) {
n.x/= normal; n.y/= normal; n.z/= normal;
}
out() = n;
}
};
Kaleidoscope
Kaleidoscope effect.


inline float lerp(float t, float a, float b) {
return (1.0f - t)*a + t*b;
}
kernel kaleidoscope: ImageComputationKernel<eComponentWise> {
Image<eRead, eAccessRandom, eEdgeClamped> in;
Image<eWrite> out;
param:
float rot, thetaTile, radiusTile, thetaOffset,
radiusOffset, thetaRange, radiusRange;
local:
float M, N, cx, cy;
void define() {
defineParam(rot, "rotation", 0.5f);
defineParam(thetaTile, "theta repeat", 4.0f);
defineParam(radiusTile, "radius repeat", 2.0f);
defineParam(thetaOffset, "theta offset", 0.5f);
defineParam(radiusOffset, "radius offset", 0.5f);
defineParam(thetaRange, "theta range", 0.5f);
defineParam(radiusRange, "radius range", 0.5f);
}
void init() {
M = in.bounds.width();
N = in.bounds.height();
cx = M*0.5f;
cy = N*0.5f;
}
void process(int2 p) {
ValueType(in) result(0);
float theta, radius, thetaOffsetRemap, radiusOffsetRemap;
// set angle and distance of pixels to polar mapping
theta = fmod((atan2(p.y - cy, p.x - cx) + PI)/(2*PI) + rot, 1.0f);
radius = 2*sqrt(pow(p.x - cx, 2) + pow(p.y - cy, 2))/N;
// start repetition settings
theta *= thetaTile;
radius *= radiusTile;
// mirror repeats
theta = fmod(floor(theta), 2.0f) == 0
? fmod(theta, 1.0f)
: 1 - fmod(theta, 1.0f);
radius = fmod(floor(radius), 2.0f) == 0
? fmod(radius, 1.0f)
: 1 - fmod(radius, 1.0f);
// offset's remapping combined with the range
thetaOffsetRemap = lerp(
clamp(thetaOffset, 0.0f, 1.0f),
clamp(thetaRange, 0.0f, 1.0f)*0.5f,
1.0f - clamp(thetaRange, 0.0f, 1.0f)*0.5f
);
radiusOffsetRemap = lerp(
clamp(radiusOffset, 0.0f, 1.0f),
clamp(radiusRange, 0.0f, 1.0f)*0.5f,
1.0f - clamp(radiusRange, 0.0f, 1.0f)*0.5f
);
// rearranges coordinates
theta = lerp(
theta,
thetaOffsetRemap - thetaRange*0.5f,
thetaOffsetRemap + thetaRange*0.5f
);
radius = lerp(
radius,
radiusOffsetRemap - radiusRange*0.5f,
radiusOffsetRemap + radiusRange*0.5f
);
// remap the coordinates for image length
theta *= M;
radius *= N;
// provide interpolation for intermediate coordinates
result += lerp(
fmod(theta, 1.0f),
in(theta, radius),
in(ceil(theta), radius)
);
result += lerp(
fmod(radius, 1.0f),
in(theta, radius),
in(theta, ceil(radius))
);
result += lerp(
fmod(theta*radius, 1.0f),
in(theta, radius),
in(ceil(theta), ceil(radius))
);
result /= 3;
// output
out() = result;
}
};
Super Shape
Provides a parametric shape based on the Superformula so it can be used as a filter in a convolution process or anything else.



inline float lerp(float t, float a, float b) {
return t <= a ? 1 : t > b ? 0 : (b - t)/(b - a);
}
kernel superShape: ImageComputationKernel<eComponentWise> {
Image<eWrite> out;
param:
float a, b, y, z, n1, n2, n3, size, rot, falloff;
local:
float M, N;
void define() {
defineParam(a, "a", 1.0f);
defineParam(b, "b", 1.0f);
defineParam(y, "y", 3.0f);
defineParam(z, "z", 3.0f);
defineParam(n1, "n1", 5.0f);
defineParam(n2, "n2", 18.0f);
defineParam(n3, "n3", 18.0f);
defineParam(size, "size", 1.0f);
defineParam(rot, "rotation", 0.5f);
defineParam(falloff, "falloff", 0.01f);
}
void init() {
M = out.bounds.width();
N = out.bounds.height();
}
void process(int2 p) {
float s, t, r, theta, radius, rMin, rMax;
s = p.x/M;
t = p.y/N;
r = sqrt(pow(0.5f - s, 2) + pow(0.5f - t, 2))*2.0f*PI/size;
theta = atan2(0.5f - t, 0.5f - s) + rot*2.0f*PI;
radius = pow(
pow(fabs(cos(theta*y/4.0f)/a), n2) +
pow(fabs(sin(theta*z/4.0f)/b), n3),
- 1.0f/n1
);
rMin = radius - falloff;
rMax = radius + falloff;
out() = lerp(r, rMin, rMax);
}
};
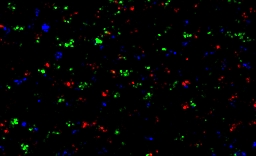
Super Convolution
Uses Superformula shapes as a convolution kernel.

inline float lerp(float t, float a, float b) {
return t <= a ? 1 : t > b ? 0 : (b - t)/(b - a);
}
kernel superConvolution: ImageComputationKernel<eComponentWise> {
Image<eRead, eAccessRandom, eEdgeConstant> in;
Image<eWrite> out;
param:
bool sample;
float a, b, y, z, n1, n2, n3, size, rot, falloff, kRad;
local:
float M, N;
void define() {
defineParam(sample, "view sample filter", false);
defineParam(a, "a", 1.0f);
defineParam(b, "b", 1.0f);
defineParam(y, "y", 3.0f);
defineParam(z, "z", 3.0f);
defineParam(n1, "n1", 5.0f);
defineParam(n2, "n2", 18.0f);
defineParam(n3, "n3", 18.0f);
defineParam(size, "size", 1.0f);
defineParam(rot, "rotation", 0.5f);
defineParam(falloff, "falloff", 0.01f);
defineParam(kRad, "kernel radius", 16.0f);
}
void init() {
M = out.bounds.width();
N = out.bounds.height();
}
void process(int2 p) {
float s, t, r, theta, radius, rMin, rMax;
if(sample) {
s = p.x/M;
t = p.y/N;
r = sqrt(pow(0.5f - s, 2) + pow(0.5f - t, 2))*2.0f*PI/size;
theta = atan2(0.5f - t, 0.5f - s) + rot*2.0f*PI;
radius = pow(
pow(fabs(cos(theta*y/4.0f)/a), n2) +
pow(fabs(sin(theta*z/4.0f)/b), n3),
- 1.0f/n1
);
rMin = radius - falloff;
rMax = radius + falloff;
out() = lerp(r, rMin, rMax);
} else {
ValueType(in) result(0);
ValueType(in) filter(0);
float2 M(p.x - kRad, p.x + kRad);
float2 N(p.y - kRad, p.y + kRad);
for(int j = N[0]; j <= N[1]; j++) {
for(int i = M[0]; i <= M[1]; i++) {
s = lerp(i, M[0], M[1]);
t = lerp(j, N[0], N[1]);
r = sqrt(pow(0.5f - s, 2) + pow(0.5f - t, 2))*2.0f*PI/size;
theta = atan2(0.5f - t, 0.5f - s) + rot*2.0f*PI;
radius = pow(
pow(fabs(cos(theta*y/4.0f)/a), n2) +
pow(fabs(sin(theta*z/4.0f)/b), n3),
- 1.0f/n1
);
rMin = radius - falloff;
rMax = radius + falloff;
filter += lerp(r, rMin, rMax);
result += lerp(r, rMin, rMax)*in(i, j);
}
}
result /= filter;
out() = result;
}
}
};